Training a segmentation Model
In this tutorial, you will learn how to train a segmentation model in Arkindex.
This section is to be followed and carried out after creating the ground-truth annotations.
Make your dataset immutable¶
The Pellet dataset created during the data partitioning step and annotated on Callico, now has three sets named train, dev and test.
To avoid any issues (data leakage, accidental deletions, …), we should lock the state of our dataset. To make it immutable, we will:
- generate an SQLite export of the project,
- save a snapshot of the elements contained in the dataset.
Generating an export of the project¶
Browse to the page of the Europeana | Pellet project. Instructions to start an SQLite export are detailed in our guide to export a project. Once started, read how to monitor the status of your export.
Wait for your export to be Done before going further in this tutorial.
Info
The SQLite export is needed to preprocess the dataset in Arkindex before training. Using an SQLite database speeds things up and avoids making too many requests to the API, especially for large datasets.
Locking the dataset¶
Once the export is ready, you will now lock the dataset.
Warning
After this operation is done, you will not be able to edit the dataset or its sets anymore.
Browse to the page of the Europeana | Pellet project and click Create training process in the Processes dropdown menu.
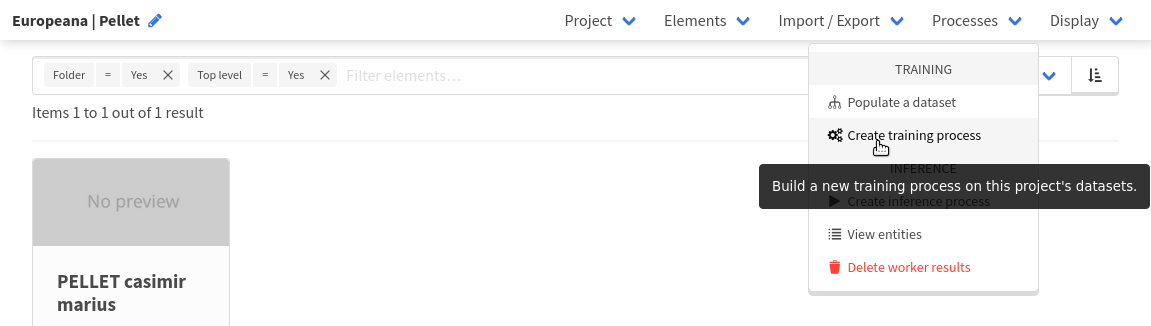
Select the Pellet dataset and select All sets to add all three sets to the process.
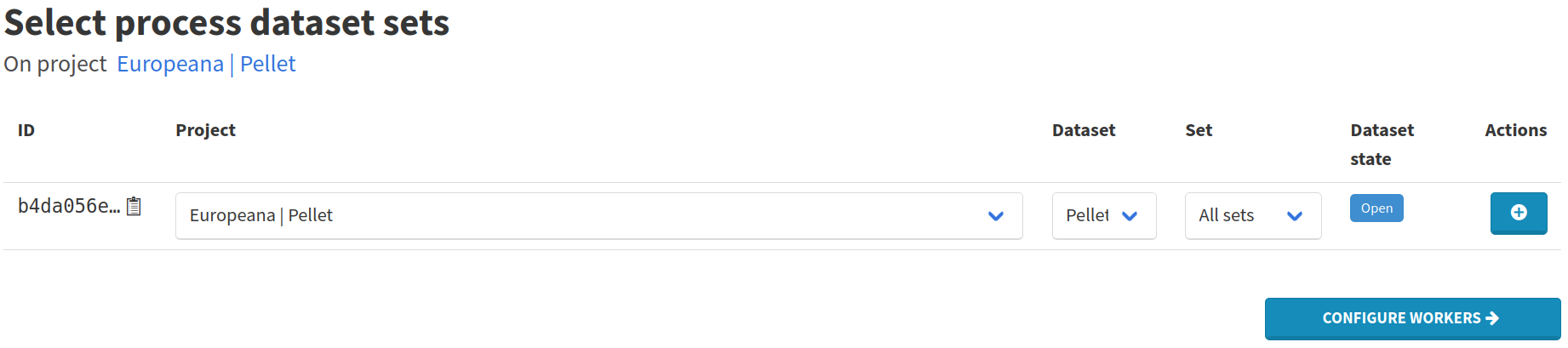
Press the button in Actions column to confirm.
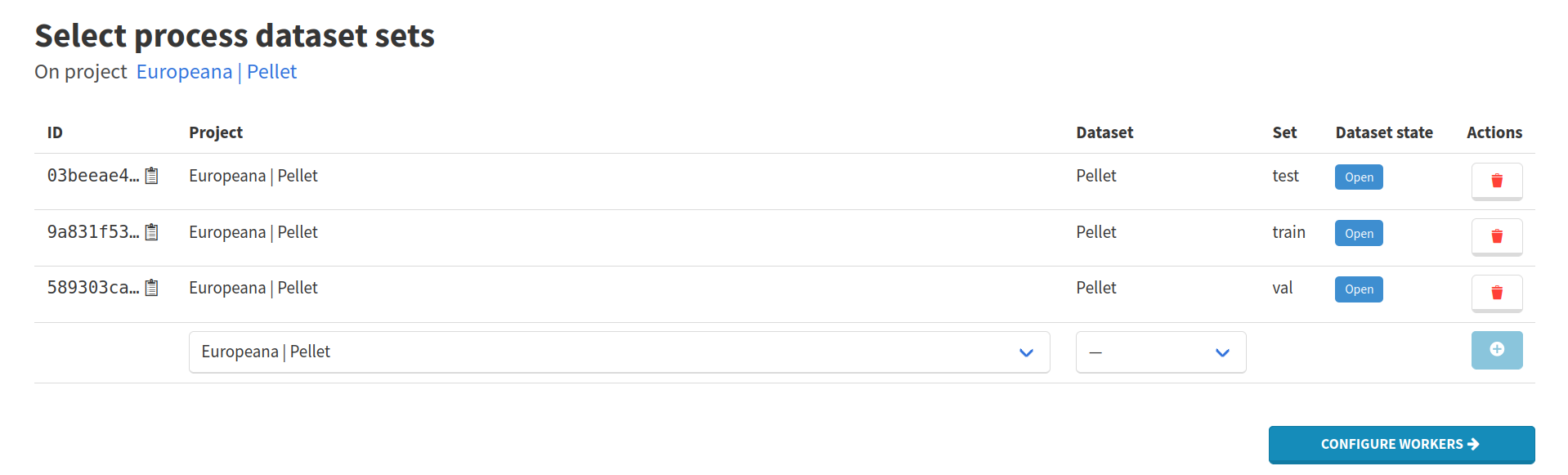
Use the Configure workers button to move on to worker selection.
Press the Select workers button, search for Generic Training Dataset Extractor and press the Enter keyboard key.
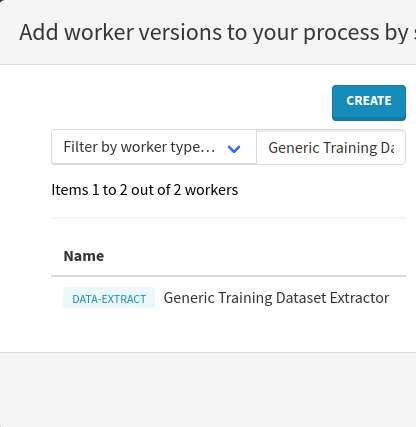
Click on the name of the worker on the left and select the recommended worker version by clicking on the Add to process button in the top-right corner.
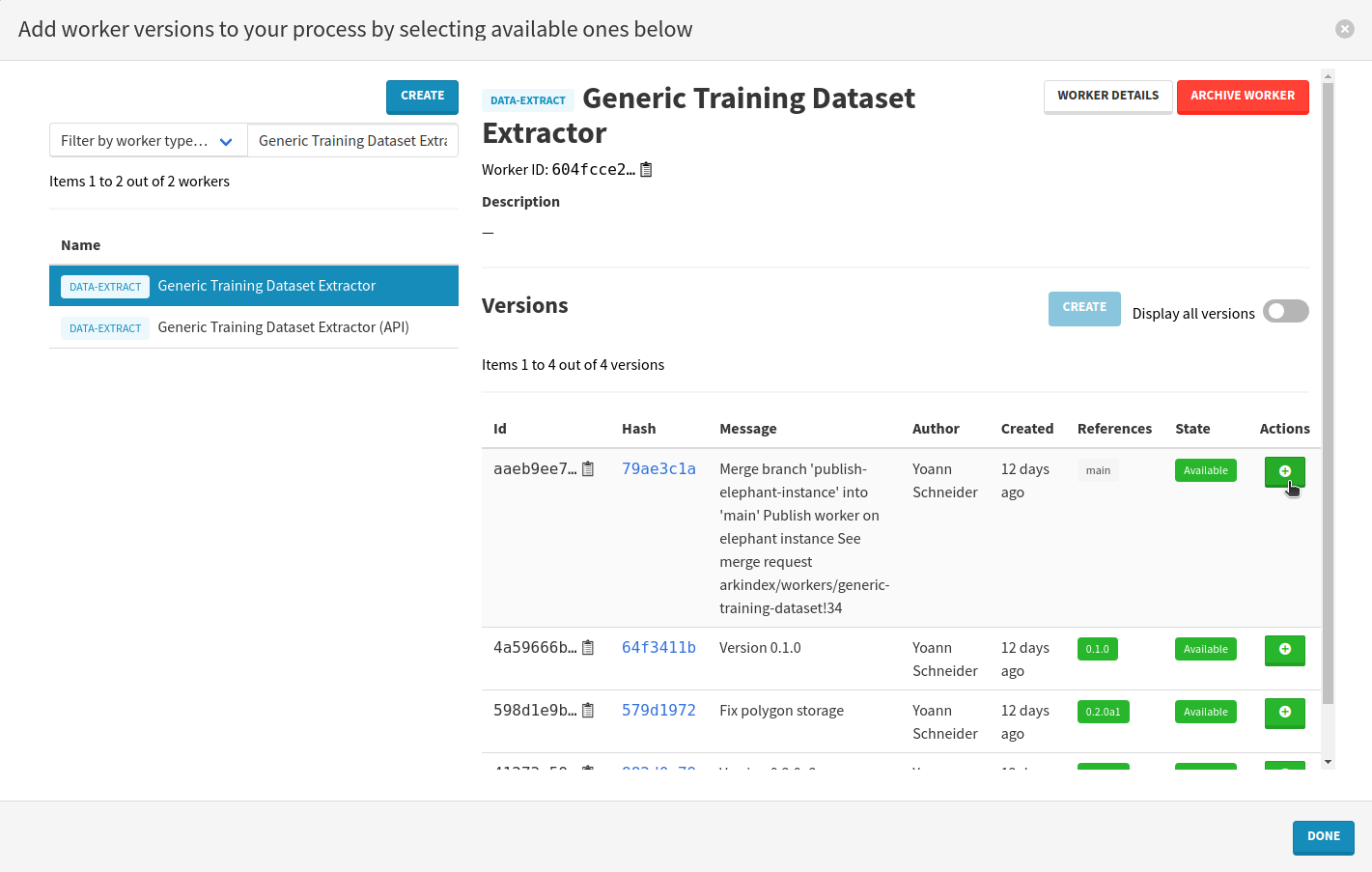
Close the modal by clicking on the Done button on the bottom right.
Your process should be configured and ready to go.
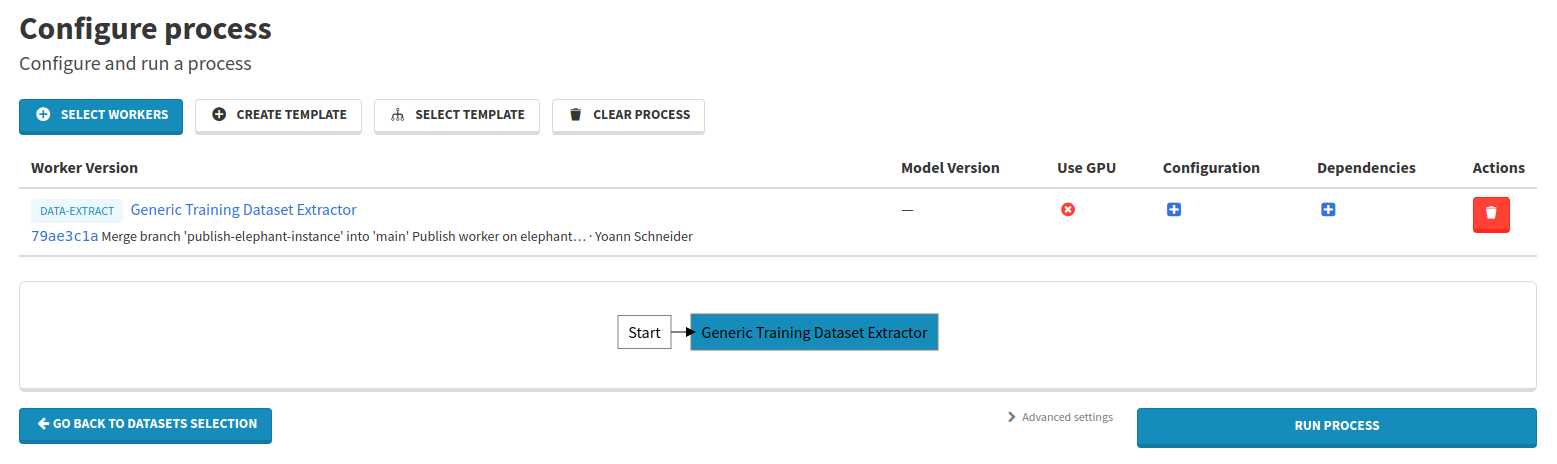
Click on the Run process button to launch the process.
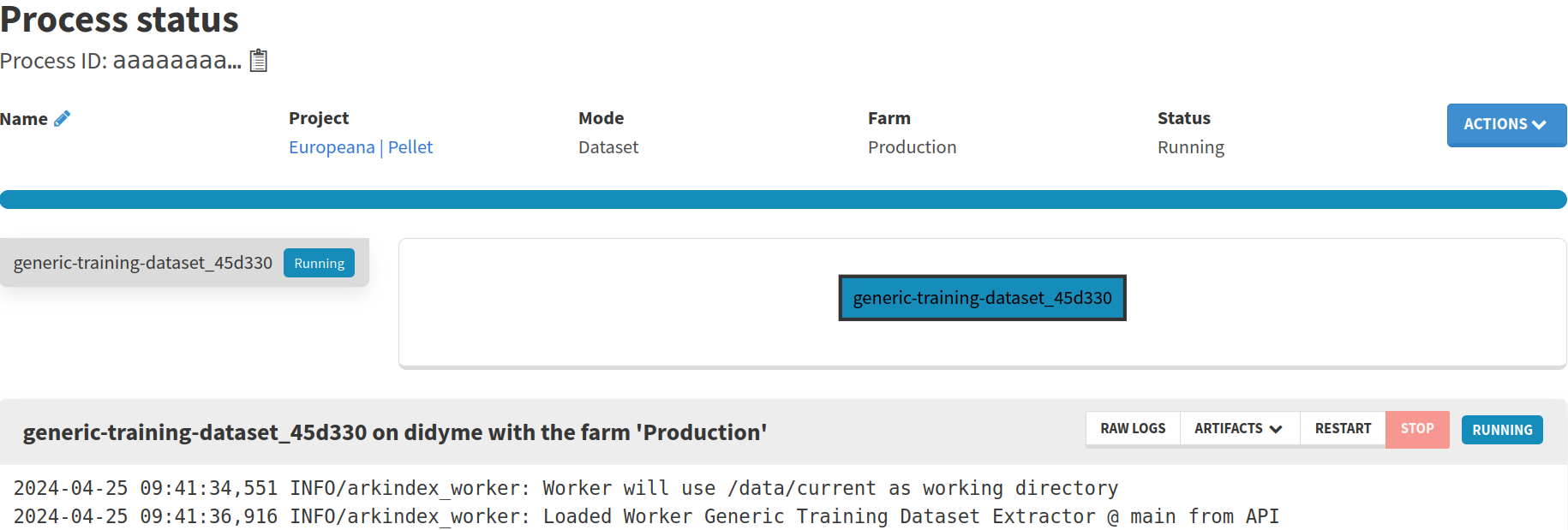
Wait till the process is over.
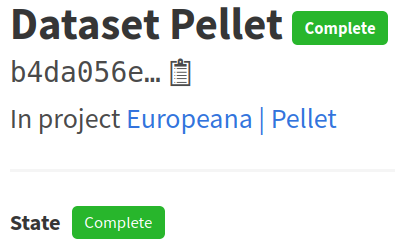
If you browse to the page of your dataset, you should see Complete next to the dataset state.
Info
This operation is only done once per dataset. If you need to train any other model on the same annotations, you will not have to regenerate the dataset like this.
However, if you added information on the elements, you will need to:
- Clone the dataset (to keep the data partitioning)
- Make that new dataset immutable, following this section’s instructions.
Create a model¶
The training will save the model’s files as a new version on Arkindex. In this section, we will create the model that will hold this new version.
Click on Models in the top right dropdown (with your email address).
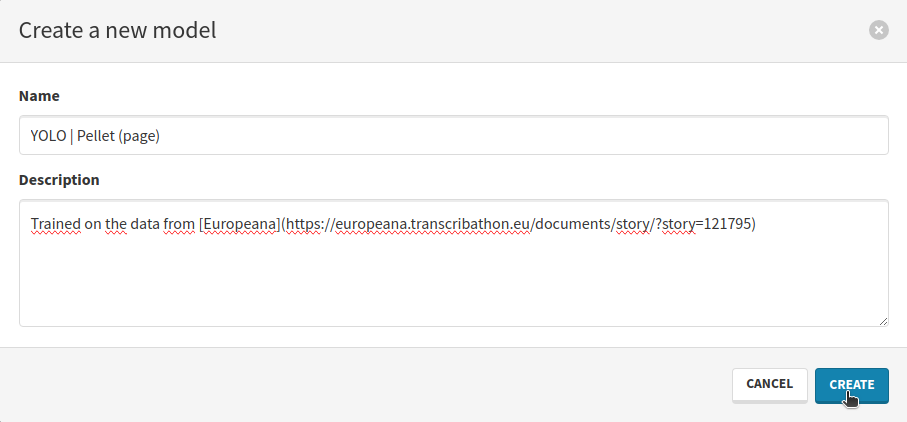
Click on the Create blue button to create a new model. This will open a modal where you can fill your model’s information. It is a good idea to name the model after:
- the Machine Learning technology used,
- the dataset,
- the type of element present in the dataset.
In our case, we are training:
- a YOLO v8 model,
- on the Pellet dataset,
- on page elements.
A suitable name would be YOLO | Pellet (page).
In the description, you can add a link towards the dataset on Europeana. The description supports Markdown input.
Info
An Arkindex model object can hold multiple versions. If you do another training under different conditions (for a longer period of time, …), you do not have to create a brand new model again.
Start your training process¶
Now that you have a dataset and a model, we can create the training process.
Create a process using all sets of the dataset. The procedure is the same as before, when we locked the dataset.
The state of the dataset has changed, you should now have the following process selection.
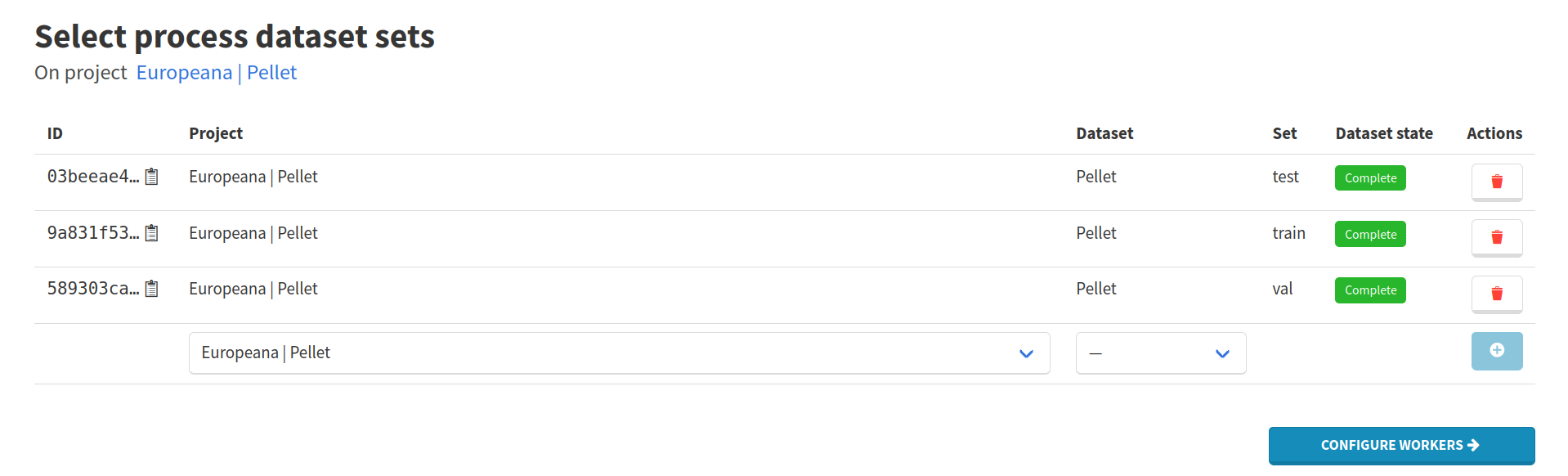
Proceed to workers configuration. Press the Select workers button, filter by the Image-segmenter worker type, then search for YOLO Training and press the Enter keyboard key.
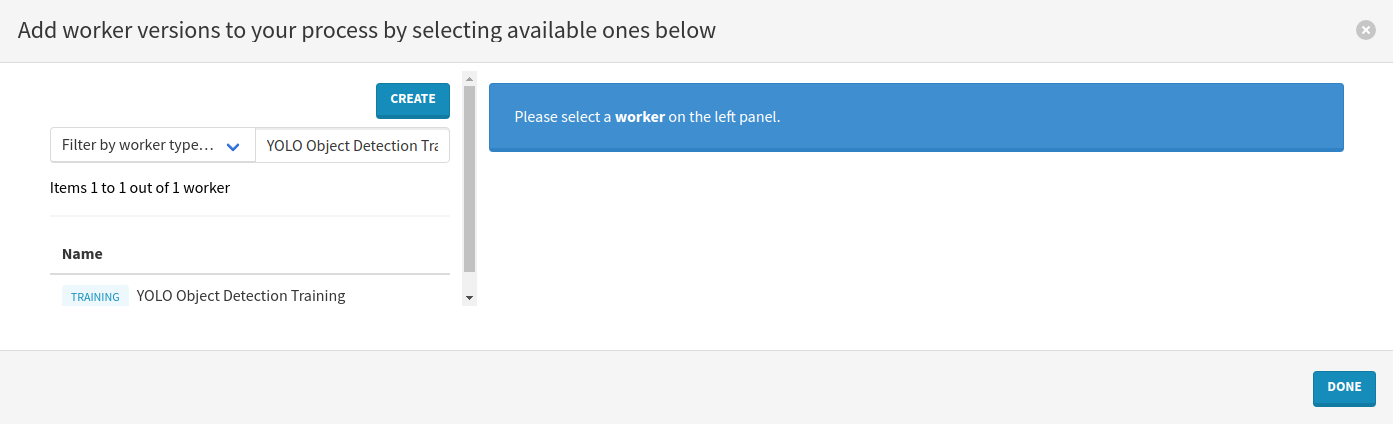
Click on the name of the worker on the left and select the recommended version by clicking on the Add to process button in the top-right corner.
Close the modal by clicking on the Done button on the bottom right.
Configure the YOLO Training worker by clicking on the button in the Configuration column. This will open a new modal, where you can pass specific parameters used for training. The full description of the fields is available on the worker’s description page.
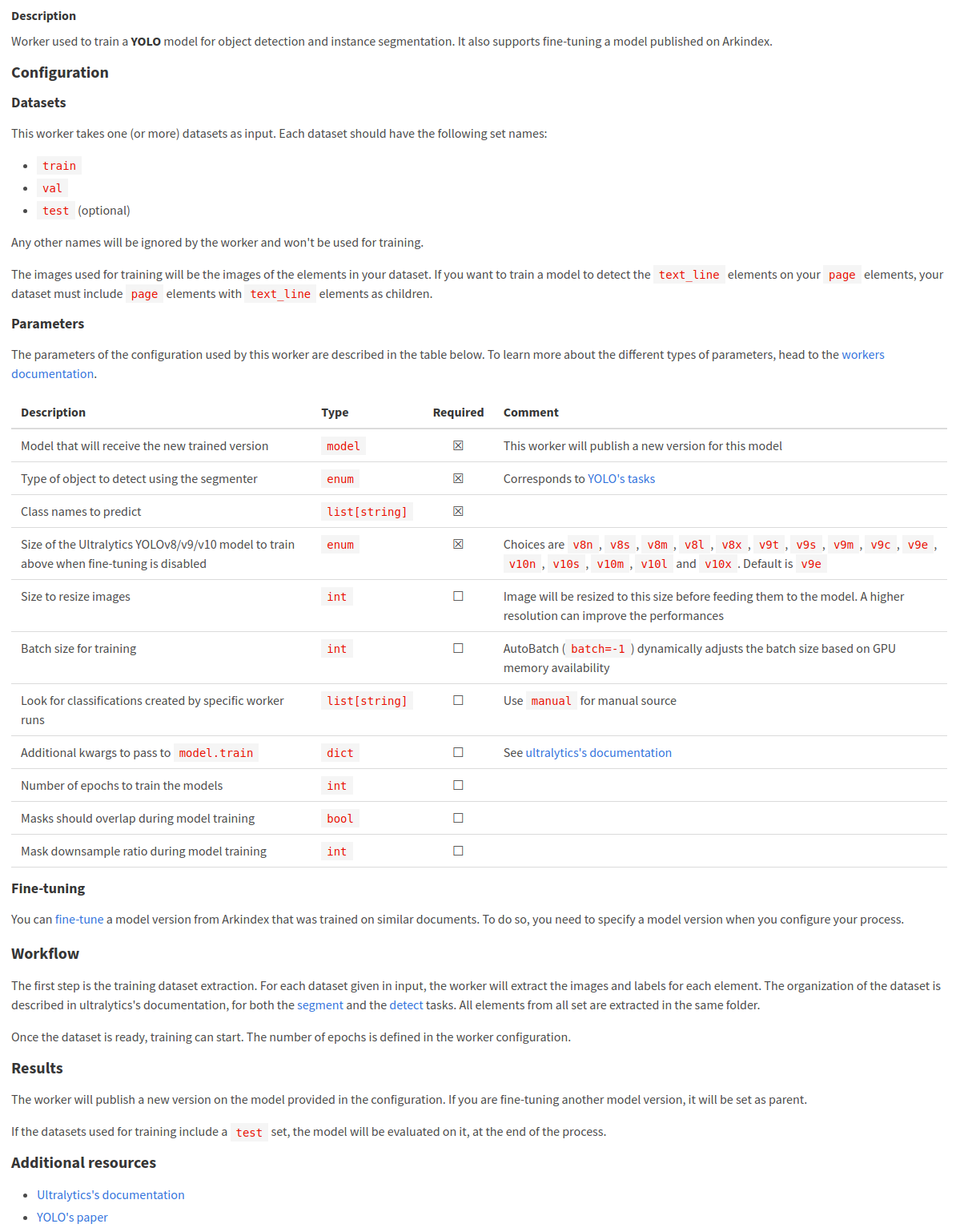
Select New configuration on the left column, to create a new configuration. Again, name it after the dataset you are using.
The most important parameters are:
- Class names to predict: add the slugs of the types that the model will predict,
text_lineandillustration, - Model that will receive the new trained version: search for the name of your model,
- Size of the Ultralytics YOLOv8/v9/v10 model: pick the medium version titled
v8mhere, - Type of object to detect using the segmenter:
- a segmenter will produce masks (polygons),
- a detector will produce bounding boxes (rectangles),
- Batch size for training (optional): a higher value will make the training faster but will also increase the memory usage,
- Number of epochs to train the model (optional): the default value is good enough but you can set it to a larger number if you want to train for a longer period of time.
Click on Create then Select when you are done filling the fields. Your process is ready to go.
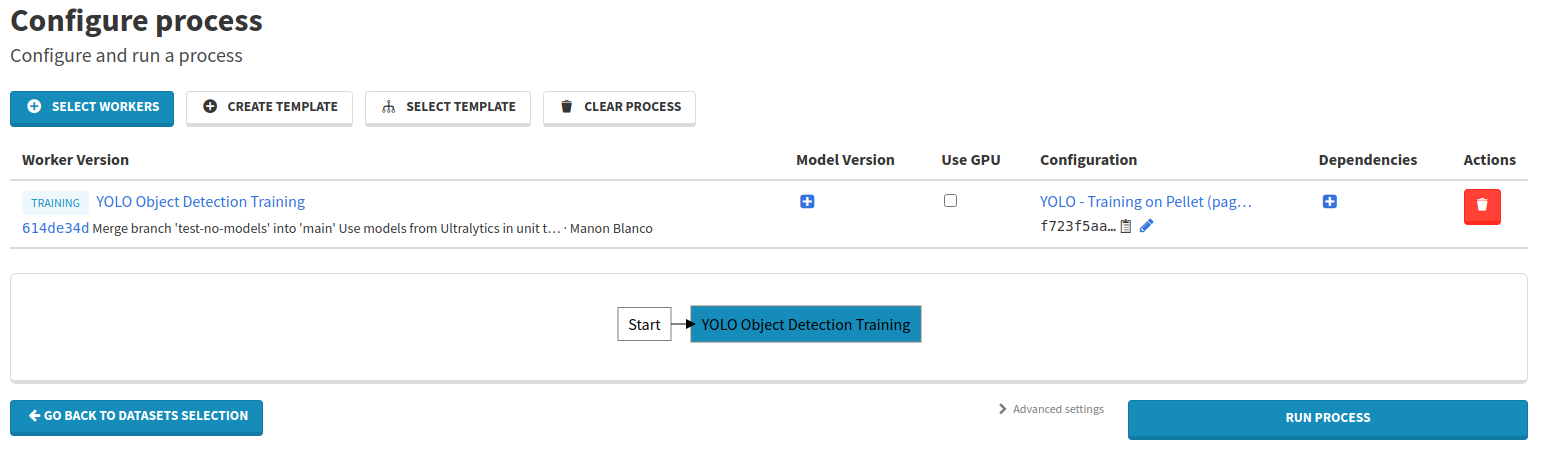
Click on the Run process button to launch the process.
While it is running, the logs of the tasks are displayed. Multiple things happen during this process:
- The dataset is converted into the right format for YOLO v8 segmentation models,
- Training starts, for as long as needed,
- Evaluation on all three splits,
- The new model is published on Arkindex.
Evaluation¶
Training logs¶
Evaluation results are displayed at the end of the training logs.
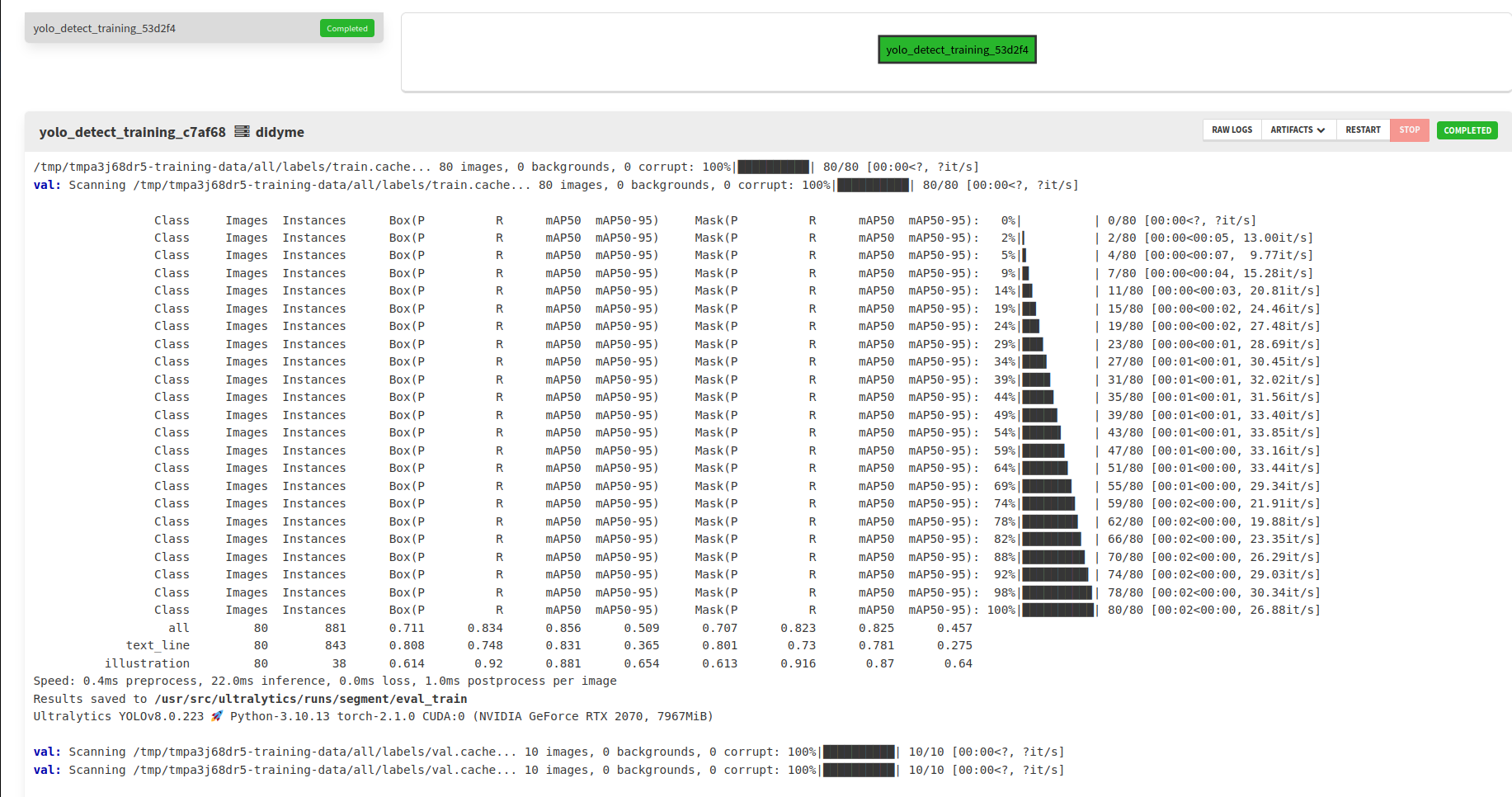
Note that YOLO uses the keyword val during the evaluation stage, even though it is run over the three splits (train, dev and test) sequentially.
To know which split is being evaluated, check the data used for the evaluation. For example, the first block (visible in the figure above) shows the performance over the train split as it loads data from /tmp/tmpa3j68dr5-training-data/all/labels/train.cache (note the train.cache at the end).
The first lines, with the progress bar, correspond to the part where the worker processed each image of the split. After that section, there is a table explaining the metrics on this split. The last line with the progress bar gives the header of the columns below.
- the
Classcolumn explains which part of the images is evaluated allcorresponds to the global performance of the model over all the examples,text_lineline corresponds to the performance of the model regardingtext_linesegmentation,illustrationline corresponds to the performance of the model regardingillustrationsegmentation.- the
Imagescolumn gives the number of pages relevant for the line, - the
Instancescolumn gives the number of objects used to compute the metric, - the next four columns relate to the evaluation of objects of type “box” (rectangles). We are mostly interested in segmentation (polygons) so we can skip these.
- the last four columns relate to the evaluation of objects of type “mask” (polygons). They correspond to the following metrics:
Pstands forPrecision. It measures the accuracy of the detected objects, indicating how many detections were correct.Rstands forRecall. It measures the ability to identify all instances of objects in the images.map50stands forMean Average Precisioncalculated at an intersection over union (IoU, i.e. overlap between predicted and actual boundary) threshold of 0.50. It measures the model’s accuracy considering only the “easy” detections.map50-95stands forMean Average Precisioncalculated at varying IoU thresholds, ranging from 0.50 to 0.95. It gives a comprehensive view of the model’s performance across different levels of detection difficulty.
We want to assess the model’s ability to generalize what it has learned to new examples. While the evaluation over the train and dev splits is relevant to make sure the model has actually learned something, only the test set contains images the model has never seen.
All metrics are important to evaluate the performance of the model. However, we generally want a high map50-95, as it provides a comprehensive evaluation of the model’s performance.
If you want more details, click the Artifacts button to list the artifacts and click results.tar.zst to download the training artifacts.
Info
This type of archive is not natively supported by Windows. In that case, you will need an external archive manager tool like 7zip.

This archive has the following file structure:
- one
trainfolder: with graphs and sheets describing how the training went, - three
eval_*folders: the evaluation results on all splits.
Make sure to take a look at these if you want to know more about your model’s performance.
Visit the page of your model to see your brand new trained model version. To do so, browse the Models page and search for your model.
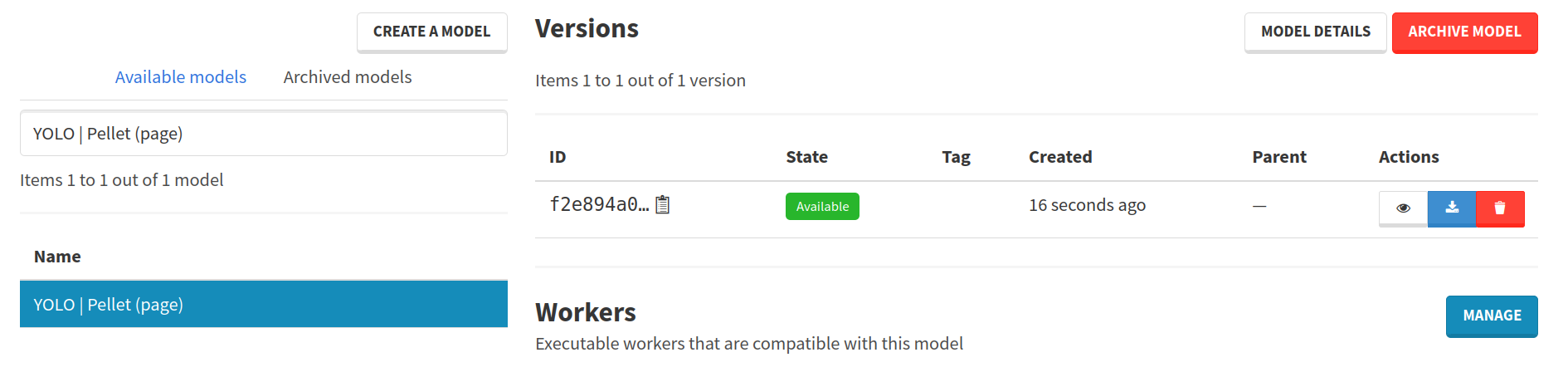
You can download it to use it on your own or to process pages already on Arkindex, as described in the next section.
Evaluation by inference¶
Graphs are nice to get an idea of how the model performs on unknown data. However, it is easier to make yourself an idea when the predictions are actually displayed.
In this section, you will learn to process the test set of your dataset with your newly trained model.
Creating the process¶
Browse to the project you created in the earlier steps of the tutorial.
Click on Create training process in the Processes menu. Select your dataset but only keep the test set.
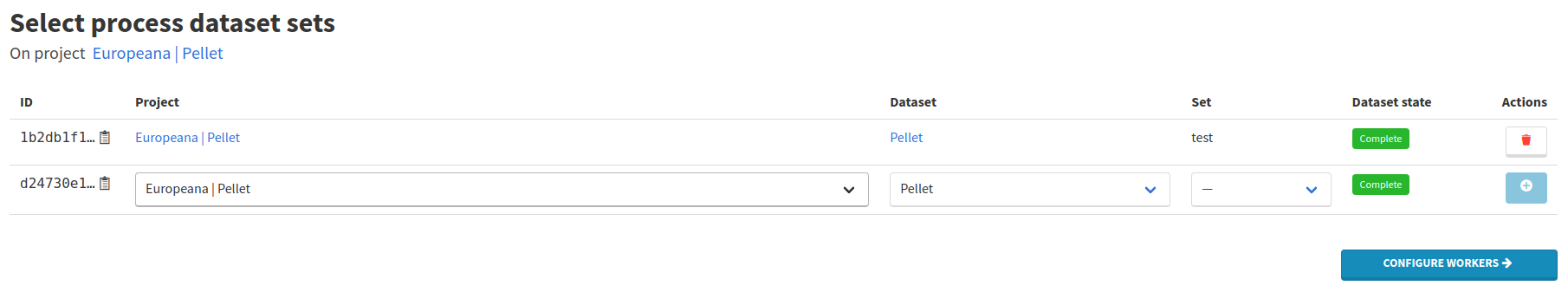
Click on Configure workers to move on to worker selection. Press the Select workers button, filter by the Image-segmenter worker type, search for YOLO Inference and press the Enter keyboard key. Just like we did in the previous sections, click on the name of the worker on the left and select the recommended version by clicking on the Add to process button in the top-right corner.
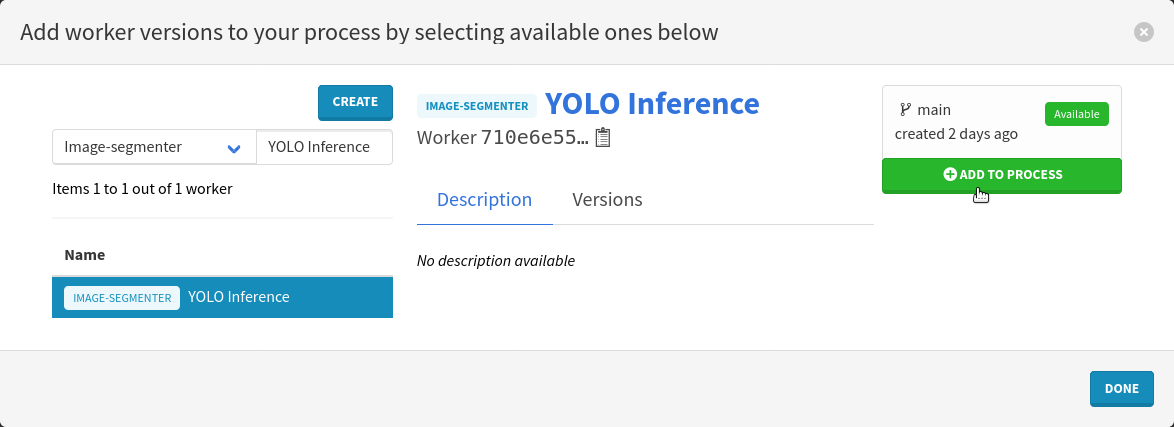
Close the modal by clicking on the Done button on the bottom right.
Now it is time to select the model you trained. Click on the button in the Model version column. In the modal that opens:
- Look for the name of your trained model,
- Add the model version by clicking on Use in the Actions column,
- Close the modal by clicking on Ok, in the bottom right corner.
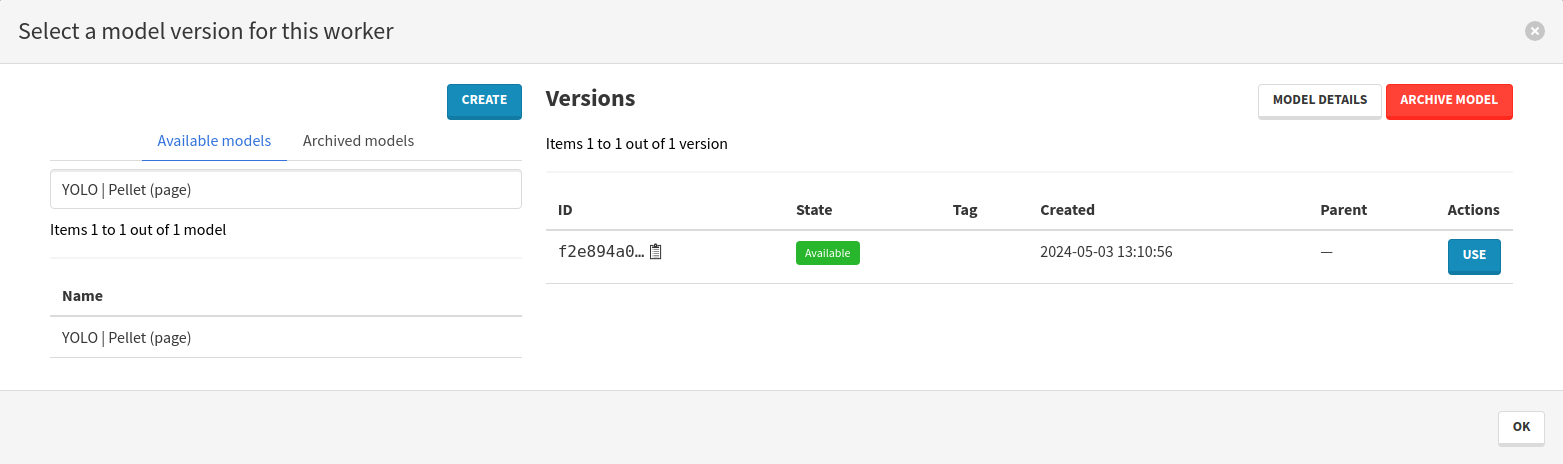
The process is ready and you can launch it using the Run process button. Wait for its completion before moving to the next step.
Visualizing predictions¶
To see the predictions of your model, browse back to the test folder in your project. There you can click on the first page displayed.
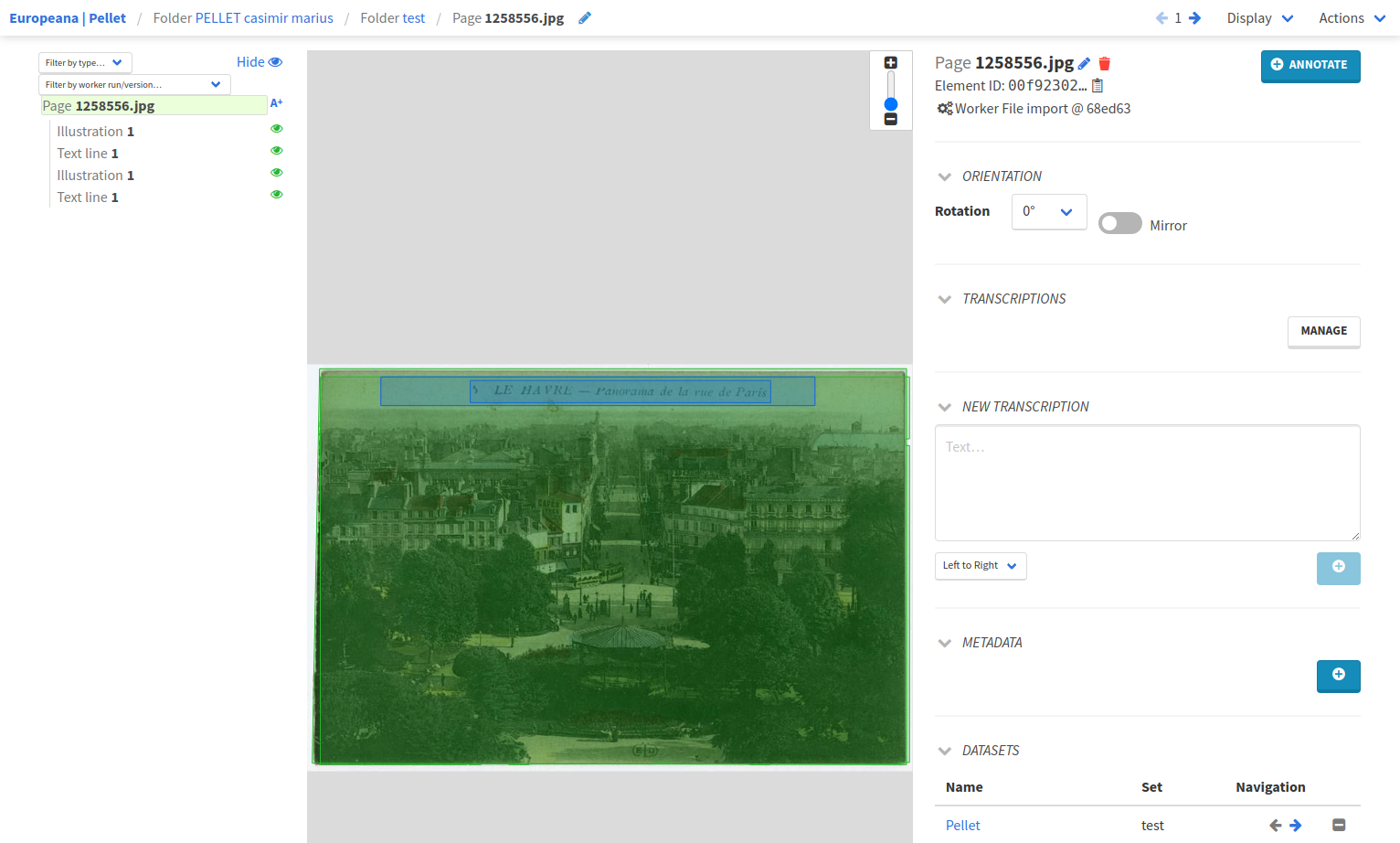
On all pages of the test set, you can see both the annotations and the predictions. To know the difference between ground truth and predictions, look at the details of each element.

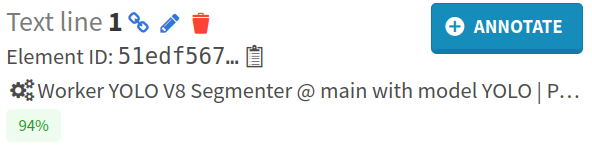
On the elements annotated by humans, Callico is mentioned. On the predicted elements, YOLO is mentioned. The confidence score of the YOLO prediction is also displayed.
Info
In this tutorial, we do not calculate evaluation scores for this segmentation model as it would require you to run scoring tools using sophisticated procedures outside the Arkindex and Callico frameworks.
Next step¶
If the model’s initial results are close to the ground truth annotations, you could use it on all your pages through a dedicated process.